How to Start Windows 10, 8(.1), 7 or XP in Safe Mode
Safe Mode is a special diagnostic mode in which Windows runs with the minimum amount of features. As the features are limited, Windows does not load unnecessary startup items and runs only those files and drivers that are necessary for the basic functioning of the operating system. This allows users to remove recently installed programs that might be preventing Windows from starting correctly. As Windows does not start unnecessary programs while in Safe Mode, it can also be used to remove viruses and malware without risking the infection getting worse.
Start Safe mode WindowsThere are different ways in which you can get into the Safe Mode in Windows. They depend on the version of Windows you are using.
In this article:
1. Steps for Windows 10, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1 users
2. Steps for Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP and previous versions
3. Force Windows to start in Safe mode
4. Which Safe Mode option should you choose?
Windows 10, Windows 8 and Windows 8.1
The F8 key method does not work on Windows 10, Windows 8 and 8.1. Hence, getting onto Safe Mode requires the following steps:-
If your PC is working properly:
1) On the Windows Start Screen/Menu, type Advanced.
2) Click on Advanced startup options.
3) Under the Advanced Startup heading at the bottom of the General Settings screen, click on Restart now.
4) Your computer will restart and you will be taken to the Advanced Startup Options menu. To easily reach this menu, on Windows start screen, you could choose restart while holding the Shift key.
5) Click on Troubleshoot and then on the Advanced Options button.
6) Now, click on Startup Settings.
7) At the Startup Settings Screen, click on Restart.
8) Your computer will restart to Advanced Boot options from where you can choose a Safe mode option based on your need.

Windows Safe mode
You can also force Windows to start in Safe mode.
If your PC is not working properly:
Windows monitors your PC's startup for problems and when an error is detected, it automatically takes you to the new Recovery mode with the message "Recovery. It looks like Windows didn't load correctly." In this case:-
1) Select Advanced Repair Options and then click on Troubleshoot.
2) Click on the Advanced Options button.
3) Now click on Startup Settings.
4) At the Startup Settings Screen, click on Restart.
5) Your computer will restart to Advance Boot Options from where you can choose a Safe mode option based on your need.
Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP and Previous versions
If you are using these versions of Windows, you can try the following methods.
The Trusted F8 key method
1) Restart your computer if it is on.
2) Right before the system starts to boot, start tapping the F8 key continuously.
3) This should load the Windows Advanced Options boot menu.
4) Select a Safe Mode option based on your need using the arrow keys and press Enter.
5) Windows will start in Safe mode. To get out of Safe mode, simply restart your computer.
This method should work on Windows 7, Windows Vista, Windows XP, Windows 2003 and Windows ME. However, if it does not, you can always force Windows to boot in Safe Mode if your computer is working "properly".
Faulty Startup Method
If the F8 key method does not take you to the Advanced options boot menu, you could try turning your computer off when it boots into Windows. Upon next restart, Windows will notice that the computer did not boot successfully and take you to the Advanced Options boot menu. Then, select a Safe mode option based on your need. This method is risky and should only be tried as a last resort. It could result in some of your files being deleted which could make your Windows installation unusable.
Force Windows to restart in Safe Mode using the System Configuration Utility
Most users looking to boot Windows in safe mode will have a computer that is not working properly. Unfortunately, this method will not help them as it requires the user to have a working computer.

Start Windows in Safe mode
Steps:
1) Press Windows key+R to load the Run dialog box.
2) Type msconfig and press Enter.
3) This will start the System Configuration Utility.
4) On Windows 10, Windows 8, Windows 7 and Windows Vista, go to the Boot tab and tick Safe Boot. On Windows XP, go to the BOOT.INI tab and tick /SAFEBOOT.
5) Click OK.
6) Click on Restart in the following dialog box to boot into Safe Mode.
7) To start your computer normally, untick the Safe Boot option in the System Configuration Utility.
Your computer will restart in Safe mode.
Different Safe Mode Options. Which to choose?
These are the various safe mode options available in Windows. You can choose one based on the features you require.

Safe Mode
This is safe mode in its most basic form without any extra features. It is useful for troubleshooting most common problems .
Safe Mode with Networking
This offers additional support of connecting to the internet or any other network. This is useful when your PC has a problem which might require you to frequently use the internet to troubleshoot.
Safe Mode with Command Prompt
This option will allow you to use all the unique features of the Windows command prompt while in Safe mode.



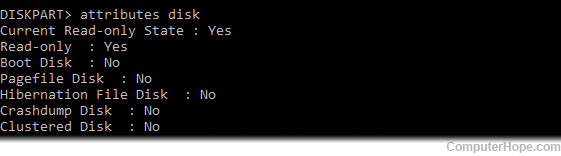
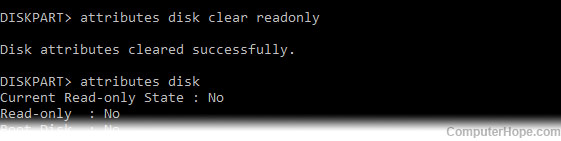
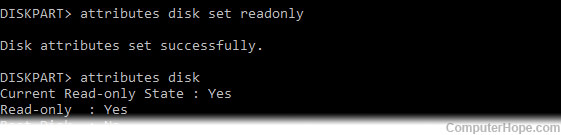



 Note
Note






















